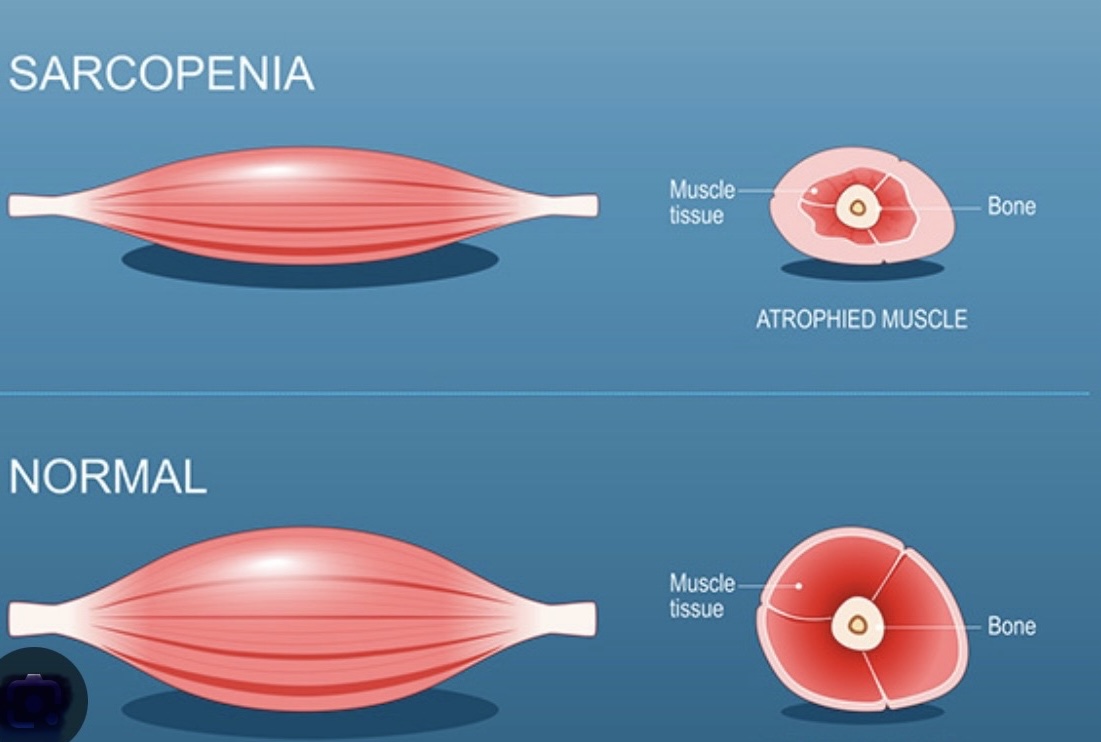
Η Σαρκοπενία είναι μια κατάσταση που χαρακτηρίζεται από την προοδευτική απώλεια μυϊκής μάζας, δύναμης και λειτουργίας, επηρεάζοντας κυρίως τους ηλικιωμένους. Αποτελεί ιδιαίτερο πρόβλημα στα απομακρυσμένα νησιά λόγω ορισμένων μοναδικών προκλήσεων, όπως η περιορισμένη πρόσβαση σε υπηρεσίες υγείας, η έλλειψη εξειδικευμένων υπηρεσιών και η φυσική απομόνωση των κατοίκων.

Σημασία της Φυσικοθεραπείας για τη Σαρκοπενία
1. Πληθυσμός Ηλικιωμένων: • Λειτουργική Αυτονομία: Η σαρκοπενία μπορεί να οδηγήσει σε αυξημένη αδυναμία, καθιστώντας δύσκολες τις καθημερινές δραστηριότητες και αυξάνοντας τον κίνδυνο πτώσεων και τραυματισμών. Αυτό είναι ιδιαίτερα προβληματικό στα απομακρυσμένα νησιά, όπου η πρόσβαση σε επείγουσα ιατρική περίθαλψη μπορεί να καθυστερήσει.
• Ποιότητα Ζωής: Η μυϊκή αδυναμία και η μειωμένη κινητικότητα μπορεί να οδηγήσουν σε κοινωνική απομόνωση και κατάθλιψη, επηρεάζοντας αρνητικά την ψυχική υγεία και τη συνολική ευεξία.

Γιώργος Γεωργάτος MCPS BSc Physiotherapy, MSc, FCP. Ashford & St Peters NHS trust
====================
English
Sarcopenia is a condition characterised by the progressive loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, predominantly affecting the elderly. It is of particular concern on remote islands due to several unique challenges, such as limited access to healthcare, fewer specialised services, and the physical isolation of residents.
Importance of Physical Therapy for Sarcopenia
1. Elderly Population: • Functional Independence: Sarcopenia can lead to increased frailty, making everyday activities difficult and increasing the risk of falls and injuries. This is especially problematic on remote islands where access to emergency medical care may be delayed. • Quality of Life: Muscle weakness and reduced mobility can lead to social isolation and depression, negatively impacting mental health and overall well-being.
2. Children: • Developmental Concerns: While sarcopenia primarily affects the elderly, children with certain medical conditions or inadequate nutrition may experience muscle weakness and delayed physical development, which can be exacerbated by limited resources and specialist care on remote islands.
• Long-term Health: Addressing muscle weakness early through physical therapy and nutrition can improve long-term health outcomes and prevent complications. Impact of Physical Therapy
1. Improving Mobility and Strength: • Exercise Programs: Physical therapists can design individualized exercise programs to improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination, essential for both elderly and children. • Fall Prevention: Strengthening exercises and balance training can significantly reduce the risk of falls, a major concern for the elderly.
2. Access to Therapy: • Challenges: On remote islands, there may be a shortage of physical therapists, and residents might have to travel long distances for regular sessions, making consistent therapy difficult. • Teletherapy Solutions: Telehealth platforms can provide remote access to therapy, offering guidance and support to patients who cannot regularly visit a physical therapist in person.
3. Community-Based Interventions:
• Group Exercise Programs: Community centers or local health initiatives can organize group exercise sessions, making physical therapy more accessible and socially engaging
. • Education and Training: Educating caregivers and family members on how to support physical therapy routines at home can enhance the effectiveness of therapy. Recommendations for Remote Islands
1. Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure: Investing in local healthcare facilities and training programs for physical therapists and other healthcare professionals.
2. Promoting Physical Activity: Encouraging community-based exercise programs and activities that promote muscle health.
3. Leveraging Technology: Utilizing telehealth and mobile health applications to provide guidance and support to individuals in remote areas.
4. Nutritional Support: Ensuring access to adequate nutrition, as it plays a critical role in maintaining muscle mass and strength. Addressing sarcopenia through physical therapy and community support is essential for improving health outcomes and quality of life for both elderly and children on remote islands.
Georgios Georgatos MCPS BSc Physiotherapy, MSc, FCP. Ashford & St Peters NHS trust
References
1. Cruz-Jentoft, A. J., et al. (2019). Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age and Ageing, 48(1), 16-31. • This paper discusses the updated consensus on the definition and diagnosis of sarcopenia and emphasizes the importance of early intervention and physical therapy for managing the condition. 2. Rolland, Y., et al. (2011). Sarcopenia: its assessment, etiology, pathogenesis, consequences, and future perspectives. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 12(7), 501-506. • Explores the causes and consequences of sarcopenia and the role of physical exercise and therapy in its management. 3. Cebrià I Iranzo, M. A., et al. (2018). Physical therapy interventions for older adults with sarcopenia: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. European Geriatric Medicine, 9(5), 563-574. • Reviews various physical therapy interventions for elderly patients with sarcopenia, highlighting their effectiveness. 4. Vernikos, J., et al. (2016). Sarcopenia in children and adolescents: new perspectives. Nutrition Reviews, 74(12), 726-736. • Discusses sarcopenia in children and the importance of physical activity and therapy in combating its onset. 5. Thomas, D. R. (2010). Sarcopenia: mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment. Journal of Nutrition in Gerontology and Geriatrics, 29(1), 10-26. • A comprehensive overview of sarcopenia, its mechanisms, and treatment options, including the role of physical therapy. 6. Fielding, R. A., et al. (2011). Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International Working Group on Sarcopenia. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 12(4), 249-256. • Highlights the prevalence of sarcopenia and the importance of early diagnosis and physical therapy intervention. 7. Verghese, J., et al. (2011). Role of physical activity in the prevention of sarcopenia in the elderly. Current Geriatrics Reports, 1(2), 1-6. • Discusses the role of physical activity and physical therapy in preventing sarcopenia among elderly populations. 8. Sousa, A. S., et al. (2020). Physical activity and sarcopenia in the elderly: a systematic review. Aging Clinical and Experimental Research, 32(2), 307-320. • This systematic review analyzes the effectiveness of physical therapy and activity in managing sarcopenia in the elderly. 9. Sayer, A. A., et al. (2013). Sarcopenia as a risk factor for falls in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporosis International, 24(4), 1079-1094. • Explores the link between sarcopenia and increased fall risk, emphasizing the need for physical therapy to improve muscle strength and balance. 10. World Health Organization (WHO). Global action plan on physical activity 2018–2030: more active people for a healthier world. • This report includes strategies for promoting physical activity globally, with specific emphasis on remote and underserved populations. These references provide a comprehensive understanding of the importance of addressing sarcopenia through physical therapy, especially in remote and underserved regions.
Georgios Georgatos MCPS BSc Physiotherapy, MSc, FCP. Ashford & St Peters NHS trust






